The development of robots has significantly advanced maintenance tasks, making them more efficient and precise. Recently, researchers at esteemed institutions such as the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, Harbin Institute of Technology, and Hong Kong University of Science and Technology have introduced a groundbreaking wireless miniature robot that can navigate through pipes and tubular structures without the need for external power sources. This innovation has the potential to revolutionize maintenance operations by minimizing damage to infrastructure and increasing efficiency.
Challenges with Current Maintenance Robots
Many existing maintenance robots rely on external power sources, limiting their application in real-world scenarios. These robots are often larger than their power-dependent counterparts, have a limited operational range, and possess fewer functionalities. As a result, tasks such as inspection, repair, and maintenance in sectors like nuclear, industrial, and medical industries become challenging. The need for a more versatile and efficient maintenance robot has prompted researchers to develop a wireless millirobot that can address these limitations.
The Innovative Design of the Wireless Millirobot
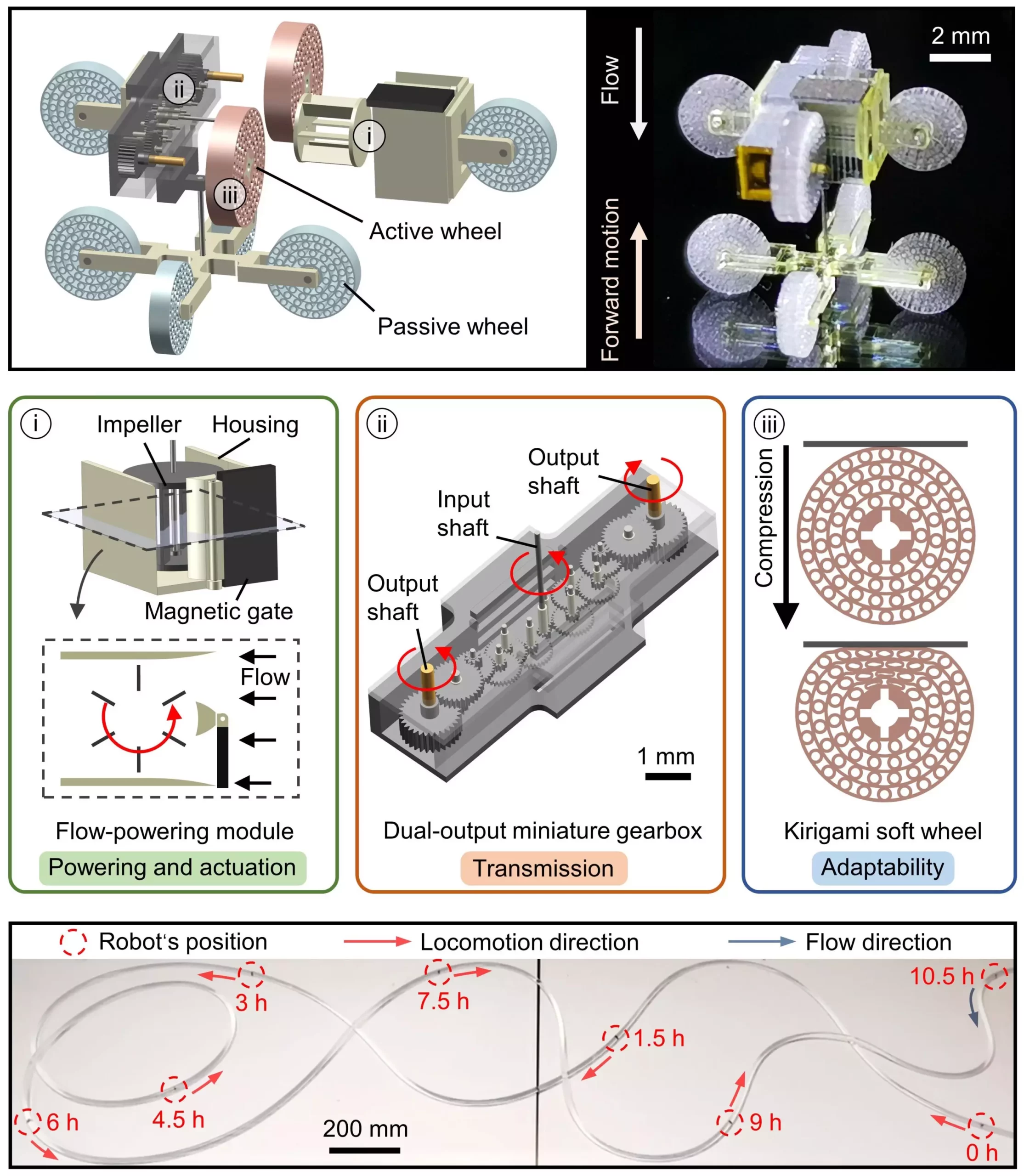
The wireless millirobot created by researchers includes an internal power source and an actuation unit, allowing it to operate autonomously within tubular structures. The robot incorporates a flow-powering module to utilize flow power, a miniature gearbox for transmitting mechanical energy, and kirigami soft wheels for adaptive locomotion. These components enable the robot to navigate through complex pipelines, covering long distances and performing maintenance tasks efficiently.
One of the key features of the millirobot is its internal impeller, which converts fluid flow in tubular structures into mechanical energy. The robot’s movement direction can be controlled by applying an external magnetic field, making it highly adaptable to different environments. Through preliminary tests, the researchers have observed promising results, indicating the robot’s ability to navigate long distances and perform tasks effectively within confined spaces. Future studies will focus on enhancing the robot’s capabilities and stability for seamless deployment in various real-world scenarios.
To ensure the robot’s efficient operation in challenging environments with high flow rates or low-friction surfaces, further improvements will be made to optimize its design. Strategies such as streamlining the robot body to reduce flow resistance and adding microstructures to the wheel surfaces for increased friction will enhance its performance. Additionally, advancements in motion status switching using external magnetic fields will be explored to enhance the robot’s functionality in diverse applications.
The development of wireless miniature robots for maintenance tasks represents a significant leap in the field of robotics. By integrating innovative design elements and advanced technologies, these robots offer a versatile and efficient solution for complex maintenance operations. With ongoing research and refinement, these robots have the potential to transform maintenance practices in various industries and pave the way for a more sustainable and effective maintenance approach.

Leave a Reply